Abstract
Background: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive malignancy that is diagnosed in approximately 60% of patients in older age. However, the early mortality and risk factors associated with elderly DLBCL are little known.
Methods: Elderly patients diagnosed with DLBCL in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database from 2000 to 2019 were selected as a trial cohort. In addition, elderly DLBCL patients from Peking University Third Hospital were used as an external validation cohort. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to identify risk factors. Nomogram models were constructed according to significant risk factors to predict overalland cancer-specific early death. In addition, the predictive value of the model was verified by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Calibration plotwas used to evaluate the calibration ability. The clinical value of nomogram was evaluated by decision curve analysis (DCA).
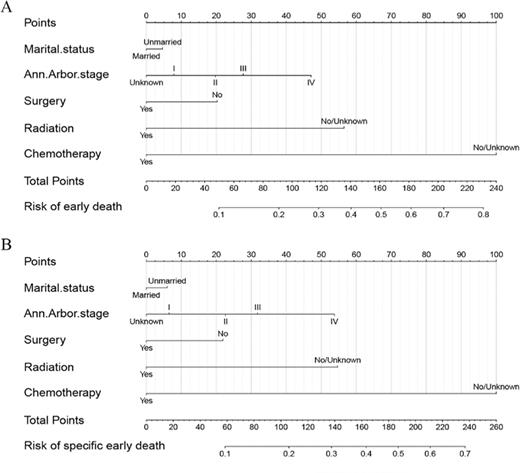
Results: A total of 15242 elderly DLBCL patients from SEER database and 152 patients from Peking University third hospital were included in this study. In the SEER database, 36.6%(5584/15242) patients had early death, and 30.7%(4680/15242) patients had cancer-specific early death. Marital status, Ann Arbor stage, surgical treatment, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are significant risk factors for overall and cancer-specific early mortality in elderly patients with DLBCL. Nomograms were constructed according to these risk factors. ROC analysis showed that the AUC of OS was 0.764 (0.756-0.772) and that of CSS was 0.742(0.733-0.751). The AUC of the verification group was 0.767 (0.689-0.846) for OS and 0.742(0.743-0.83) for CSS. The calibration plots and DCA analysis showed that the model had good early death prediction and clinical application value.
Conclusion: This study establishes and validates a predictive nomogram model for elderly diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, which plays an important role in making better treatment strategies for physicians.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.